Installing AREDN® Firmware¶
The steps for installing device firmware are documented on the AREDN® website in the Current Software section. Under the Software menu, select Download to reach the Current Software page.
There are two cases for installing AREDN® firmware:
- If you already have an existing version of AREDN® running on your device, then you can use your computer’s web interface to navigate to Setup > Administration > Firmware Update to install your new firmware. This process will be explained in more detail in the Advanced Configuration section of this guide.
If you are installing AREDN® firmware on a device for the first time, each hardware platform may require a unique procedure.
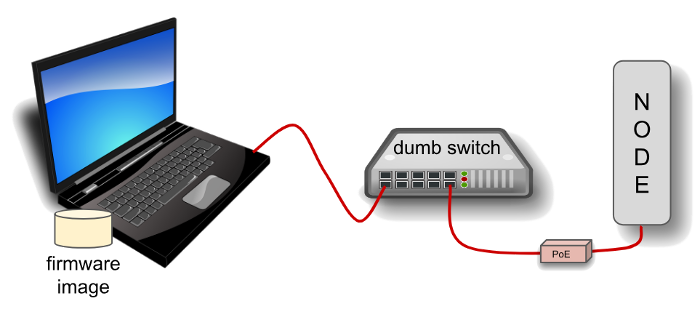
The diagram above shows that your computer with the downloaded firmware image must be connected to the node using Ethernet cables in order to install the AREDN® image. It is helpful to connect the computer and node through a simple Ethernet switch so that the switch can maintain the computer’s link while the node is being rebooted.
Different node hardware will require different methods for installing the AREDN® firmware. For Ubiquiti devices, your computer’s TFTP client will connect to the node’s TFTP server in order to upload the firmware image. For TP-LINK devices, your computer’s web browser will connect to the node’s web server to upload the firmware image. For Mikrotik devices, your computer will run a remote boot server and the node’s remote boot client will load its boot image from your computer. Refer to the specific procedures below for your node hardware.
Ubiquiti First Install Process¶
Ubiquiti devices have a built-in TFTP server to which you can upload the AREDN® factory image. Your computer must have TFTP client software available. Linux and Mac both have native TFTP clients, but you may need to enable or obtain a TFTP client for Windows computers. If you are using a Windows computer, enable the TFTP client or download and install a TFTP command line client.
Download the appropriate factory file for your device by following the instructions in the Downloading AREDN Firmware section of this documentation.
- Set your computer’s Ethernet network adapter to a static IP address of 192.168.1.5 with a netmask of 255.255.255.0
- Connect an Ethernet cable from your computer to the dumb switch, and another cable from the LAN port of the PoE adapter to the switch.
- Put the Ubiquiti device into TFTP mode by holding the reset button while plugging your node’s Ethernet cable into the POE port on the PoE adapter.
- Continue holding the device’s reset button for approximately 30 to 45 seconds until you see the LEDs on the node alternating in a 1-3, 2-4, 1-3, 2-4 pattern, then release the reset button.
- Open a command window on your computer and execute the following commands to send the AREDN firmware to your device:
>>> > tftp 192.168.1.20 [If your device is an AirRouter use 192.168.1.1] > bin [This puts the transfer in the required "binary" mode] > trace on [This will show the transfer in progress] > put <full path to the AREDN firmware file> [For example, put c:\temp\aredn-3.19.3.0-ubnt-nano-m-xw-factory.bin]The TFTP client should indicate that data is being transferred and eventually completes.
- Watch the LEDs for about 2-3 minutes until the node has finished rebooting. The reboot is completed when the LED 4 light (farthest on the right) is lit and is steady green.
- Configure your computer’s Ethernet network interface to use DHCP for obtaining an IP address from the node.
- After the node reboots, open a web browser and enter the following URL:
http://localnode.local.mesh:8080 - Navigate to the Setup page and configure the new “firstboot” node as described in the Basic Radio Setup section.
TP-LINK First Install Process¶
Preferred Process¶
TP-LINK devices currently allow you to use the manufacturer’s pre-installed PharOS web browser user interface to upload and apply new firmware images. This is the most user-friendly way to install AREDN® firmware. Navigate to the Setup section to select and upload new firmware. Check the TP-LINK documentation for your device if you have questions about using their built-in user interface.
Alternate Process¶
TP-LINK devices also have a built-in TFTP and Bootp client which allows them to obtain new firmware from an external source. Your computer must run a TFTP/Bootp server in order to provide firmware images to the node. In certain situations you may need to use this method to update the firmware or to restore a TP-LINK recovery file by following the steps below.
Preparation
- Download the appropriate TP-LINK factory file and rename this file as
recovery.bin - Set your computer’s Ethernet network adapter to a static IP address of 192.168.0.100 with a netmask of 255.255.255.0
- Connect an Ethernet cable from your computer to the dumb switch, and another cable from the LAN port of the PoE adapter to the switch.
Linux Procedure
- Create a directory on your computer called
/tftpand copy the TP-LINKrecovery.binfile there. - Determine your computer’s Ethernet interface name with
ifconfig. It will be the interface you set to 192.168.0.100 above. You will use this interface name in the command below as the name after-iand you must substitute your login user name after-ubelow. - Become
rootand open a terminal window to execute the following dnsmasq command:
>>>
# dnsmasq -i eth0 -u joe --dhcp-range=192.168.0.150,192.168.0.200 \
--dhcp-boot=recovery.bin --enable-tftp --tftp-root=/tftp/ \
-d -p0 -K --log-dhcp --bootp-dynamic
- With the PoE unit powered off, connect an Ethernet cable from the TP-LINK node to the POE port.
- Push the reset button on the TP-LINK and hold it while powering on the PoE unit. Continue to hold the reset button until you see output information from the computer window where you ran the dnsmasq command, which should happen after about 10 seconds. Release the reset button as the computer starts communicating with the node. When you see the “sent” message, this indicates success, and the TP-LINK node has downloaded the image and will reboot. You can now <ctrl>C or kill dnsmasq.
Windows Procedure
You will need Tiny PXE software on your Windows computer. Download this software and extract it on your computer.
- Navigate to the folder where you extracted the Tiny PXE software and edit the
config.inifile. Directly under the[dhcp]tag, add the following line:rfc951=1then save and close the file. - Copy the
recovery.binfirmware image into thefilesfolder under the Tiny PXE server directory location. - Start the Tiny PXE server exe and select your Ethernet interface IP from the dropdown list called
Option 54 [DHCP Server], making sure to check theBind IPcheckbox. Under the “Boot File” section, enterrecovery.bininto the the Filename field, and uncheck the checkbox for “Filename if user-class = gPXE or iPXE”. Click the Online button at the top of the Tiny PXE window.
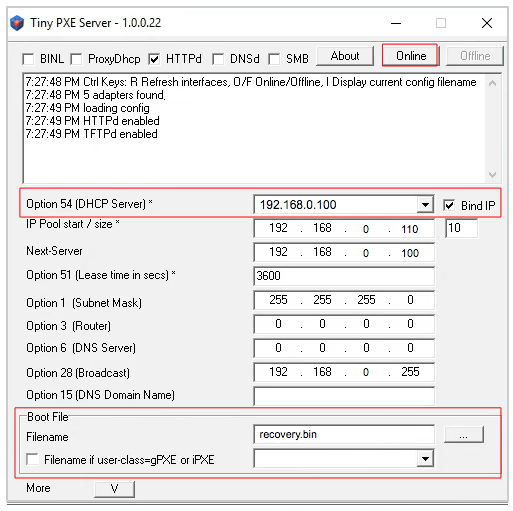
- With the PoE unit powered off, connect an Ethernet cable from the TP-LINK node to the POE port. Press and hold the reset button on the node while powering on the PoE unit.
- Continue holding the reset button until you see
TFTPd: DoReadFile: recovery.binin the Tiny PXE log window. - Release the node’s reset button and click the Offline button in Tiny PXE. You are finished using Tiny PXE when the firmware image has been read by the node.
Final Configuration Steps
- Configure your computer’s Ethernet network interface to use DHCP for obtaining an IP address from the node.
- After the node reboots, open a web browser and enter the following URL:
http://localnode.local.mesh:8080 - Navigate to the Setup page and configure the new “firstboot” node as described in the Basic Radio Setup section.
Mikrotik First Install Process¶
Mikrotik devices must be flashed using steps that are similar to the alternate TP-LINK process described above. Your computer must run a TFTP/Bootp server in order to provide firmware images to Mikrotik nodes. Mikrotik nodes require a two-part install process: First, install and boot the factory (elf) file, and finally use the in-memory-only AREDN® Administration UI to complete the installation of the sysupgrade (bin) file.
Preparation
- Download the appropriate Mikrotik factory and sysupgrade files. Rename the factory file to
rb.elfand keep the sysupgrade file available for later. - Set your computer’s Ethernet network adapter to a static IP address of 192.168.1.10 with a netmask of 255.255.255.0
- Connect an Ethernet cable from your computer to the dumb switch, and another cable from the LAN port of the PoE adapter to the switch. If you are flashing a Mikrotik hAP ac lite device, connect the Ethernet cable from Port 1 of the Mikrotik to the dumb switch.
Linux Procedure
- Create a directory on your computer called
/tftpand copy therb.elffile there. - Determine your computer’s Ethernet interface name with
ifconfig. It will be the interface you set to 192.168.1.10 above. You will use this interface name in the command below as the name after-iand you must substitute your login user name after-ubelow. - Become
rootand open a terminal window to execute the following dnsmasq command:
>>>
# dnsmasq -i eth0 -u joe --dhcp-range=192.168.0.100,192.168.0.200 \
--dhcp-boot=rb.elf --enable-tftp --tftp-root=/tftp/ \
-d -p0 -K --log-dhcp --bootp-dynamic
- With the PoE unit powered off, connect the Mikrotik node to the POE port. Press and hold the reset button on the Mikrotik while powering on the PoE unit or the hAP device.
- Continue to hold the reset button until you see output information from the computer window where you ran the dnsmasq command, which should happen after about 10 seconds. Release the reset button as the computer starts communicating with the node. When you see the “sent” message, this indicates success, and the node has downloaded the image and will reboot. You can now <ctrl>C or kill dnsmasq.
Windows Procedure
You will need Tiny PXE software on your Windows computer. Download this software and extract it on your computer.
- Navigate to the folder where you extracted the Tiny PXE software and edit the
config.inifile. Directly under the[dhcp]tag, add the following line:rfc951=1then save and close the file. - Copy the
rb.elffile into thefilesfolder under the Tiny PXE server directory location. - Start the Tiny PXE server exe and select your Ethernet interface IP from the dropdown list called
Option 54 [DHCP Server], making sure to check theBind IPcheckbox. Under the “Boot File” section, enterrb.elfinto the the Filename field, and uncheck the checkbox for “Filename if user-class = gPXE or iPXE”. Click the Online button at the top of the Tiny PXE window. - With the PoE unit powered off, connect the Mikrotik node to the POE port. If you are flashing a Mikrotik hAP ac lite device, connect the LAN cable from Port 1 of the Mikrotik to the dumb switch.
- Press and hold the reset button on the node while powering on the PoE unit or the device. Continue holding the reset button until you see
TFTPd: DoReadFile: rb.elfin the Tiny PXE log window. - Release the node’s reset button and click the Offline button in Tiny PXE. You are finished using Tiny PXE when the firmware image has been read by the node.
Final Configuration Steps
- After booting the AREDN firmware image the node should have a default IP address of 192.168.1.1. Change your computer’s Ethernet interface to DHCP mode to obtain an IP address from the node. You should be able to ping the node at 192.168.1.1. If this does not work, then something is wrong. Don’t proceed until you can ping the node.
- In a web browser, open the node’s Administration page http://192.168.1.1:8080/cgi-bin/admin (user = ‘root’ password = ‘hsmm’) and navigate to the Setup > Administration > Firmware Update section. Select the sysupgrade file you previously downloaded and click the Upload button.
- After the node reboots, navigate to the node’s Setup page and configure the new “firstboot” node as described in the Basic Radio Setup section.
Once your device is running AREDN® firmware, you can display its web interface by connecting your computer to the LAN port on the PoE and navigating to the following URL: http://localnode:8080
By default AREDN® devices run the DHCP service on their LAN interface, so your computer will receive an IP address from the node as soon as it is connected with an Ethernet cable. Ensure that your computer is set to obtain its IP address via DHCP.